Now Reading: Dying star’s “beforehand unseen layers” seen in new Webb house telescope picture
-
01
Dying star’s “beforehand unseen layers” seen in new Webb house telescope picture
Dying star’s “beforehand unseen layers” seen in new Webb house telescope picture

Spectacular new photos from NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope gave astronomers an in depth, never-before-seen take a look at a dying star.
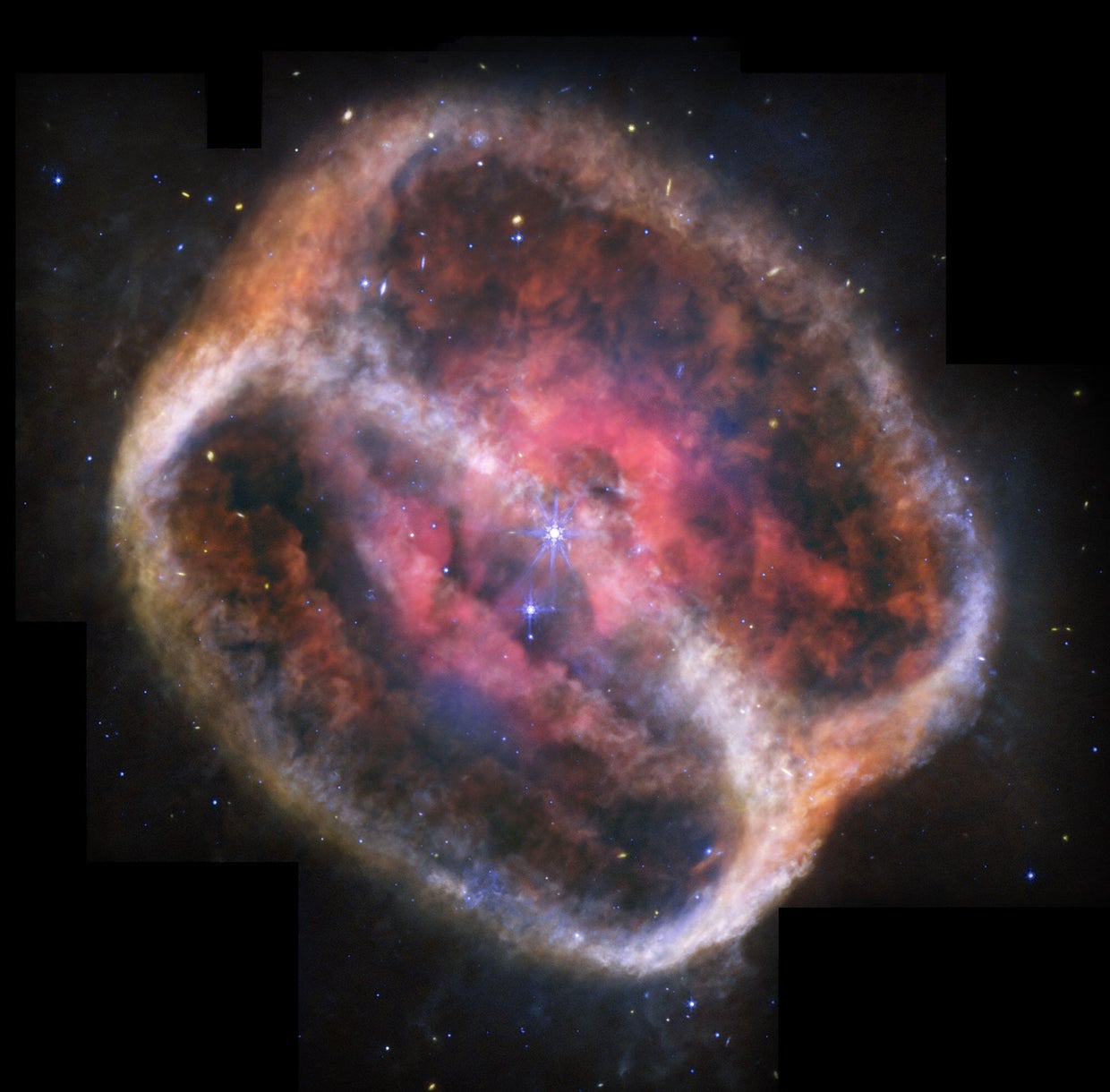
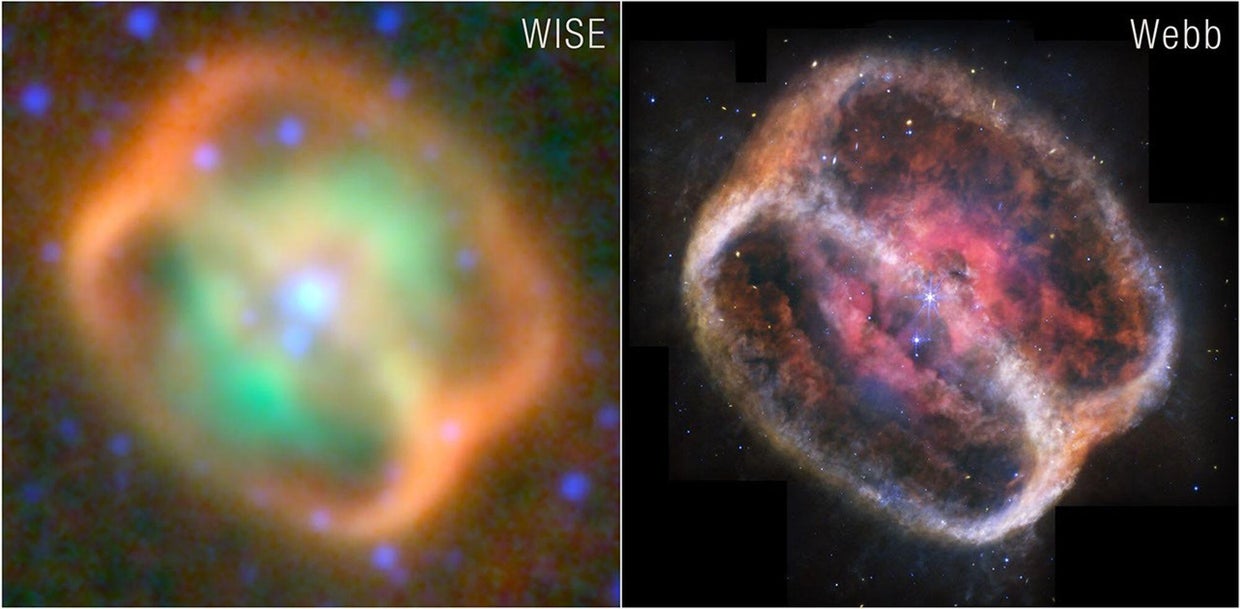
The star is definitely considered one of two on the coronary heart of NGC 1514, a nebula within the Taurus constellation about 1,500 light-years from Earth, NASA stated in a information launch. It’s a white dwarf star that was as soon as “a number of occasions extra large” than the Earth’s solar. It has been within the means of dying for over 4,000 years, and “will proceed to vary over many extra millennia,” the house company stated.
The celebs are surrounded by diffraction spikes, that are the starburst-like radiating traces that seem round shiny objects on telescope photos. The celebs comply with a nine-year orbit and are surrounded by mud. The mud seems orange within the photos.
The gradual decay of the star created a lot of the photo voltaic materials seen within the new photos.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Michael Ressler (NASA-JPL), Dave Jones (IAC)
“Because it advanced, it overvalued, throwing off layers of fuel and dirt in a really gradual, dense stellar wind,” stated David Jones, a senior scientist on the Institute of Astrophysics on the Canary Islands, within the information launch. It was Jones who decided that there have been really two stars on the heart of the show.
With the Webb Telescope’s mid-infrared instrument, or MIRI, researchers had been in a position to seize photos of the star ejecting fuel and dirt in full focus. They had been additionally in a position to seize photos of rings across the stars, which may solely be seen with infrared mild. The rings, imaged as fuzzy clumps in tangled patterns, could not be seen on digicam till now, stated Mike Ressler, a researcher and MIRI mission scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory who found the rings in 2010.
“Earlier than Webb, we weren’t in a position to detect most of this materials, not to mention observe it so clearly,” stated Ressler within the information launch. “With MIRI’s information, we will now comprehensively study the turbulent nature of this nebula.”
Ressler stated he and different researchers imagine the rings are “primarily made up of very small mud grains” which can be heated by ultraviolet mild from the dying white dwarf star. That warmth would trigger the grains to be simply heat sufficient to be detected by the MIRI, Ressler stated.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, NASA-JPL, Caltech, UCLA, Michael Ressler (NASA-JPL), Dave Jones (IAC)
The nebula seems to be tilted at a 60-degree angle, however NASA stated it is extra seemingly it “takes the form of an hourglass with the ends lopped off.” That is indicated by the shallow V-shapes created by among the mud, NASA stated.
The telescope photos additionally confirmed oxygen, which is seen as pink clumps on the edges of bubbles or holes. The MIRI additionally captured a shiny blue star to the decrease left. This small star is way nearer to Earth than the celebrities on the coronary heart of NGC 1514, and isn’t a part of the nebula.
There are additionally some notable issues lacking from the scene, NASA stated. Carbon and its complicated cousin, polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons, are widespread in nebulas like this, however neither had been detected inside NGC 1514. This can be as a result of the complicated molecules couldn’t type due to the celebrities’ orbit. The shortage of those supplies is a part of why the sunshine from each stars reaches additional, permitting the rings to be seen.